Celiac disease, also called gluten-sensitive enteropathy, is a lifelong intolerance to specific proteins found in rye, wheat, and barley, collectively known as gluten. For individuals with this disease, having a strict gluten-free diet is mandatory to prevent damage to the small intestine and alleviate symptoms. However, whether oats, a naturally gluten-free grain, are safe for celiacs has sparked debate in recent years. Let’s find an answer by studying the research studies!
What is a Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease, also called gluten-sensitive enteropathy, is an autoimmune disorder characterized by a reaction to gluten, found in rye, wheat, and barley. When individuals having celiac disease eat food containing gluten, their body’s immune system mistakenly attacks their small intestine lining, causing damage to the small intestinal villi. This damage impairs the absorption of nutrients from food, resulting in various symptoms and nutritional deficiencies.
What is Gluten Sensitivity?
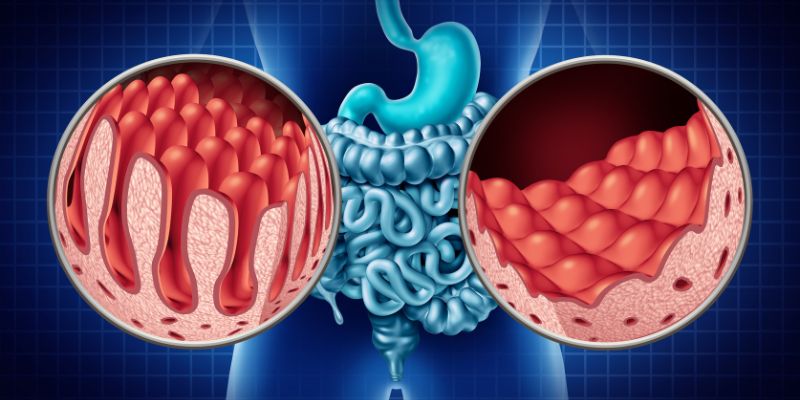
Gluten, comprised of specific storage proteins such as gliadin in wheat, hordein in barley, and secalin in rye, is central in triggering the autoimmune response in celiac disease. For individuals genetically predisposed to the condition, the ingestion of gluten creates an immune reaction that damages the delicate mucosal lining of the small intestine. Over time, this damage can lead to various symptoms, including gastrointestinal discomfort, diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and malabsorption of nutrients like iron, calcium, and vitamins.
What are Oats?
Oats, scientifically known as Avena sativa, are a cereal grain commonly consumed worldwide. They have gained popularity not only for their nutritional value but also for their versatility in various culinary applications. Oats are not only tasty but also pack a punch for nutrition. They're like tiny powerhouses of vitamins and minerals, making them a fantastic addition to anyone's diet, especially for those with celiac disease.
Vitamins and Minerals:
Oats contain essential vitamins and minerals that our bodies need to stay healthy. They include things like vitamin B, which helps keep our energy levels up, and minerals like iron, essential for our blood.
Protein Content:
Surprisingly, oats also contain a lot of protein, essential for building and repairing muscles. They have about twice as much protein as rice, which is impressive for such a humble grain.
Easy to Digest:
The starch in oats is super easy for our bodies to break down, so we can get all those nutrients without any tummy troubles. Plus, the dietary fiber in oats helps keep our digestion running smoothly.
Heart Health:
One of the most incredible things about oats is their ability to help keep our hearts healthy. They're enriched in soluble fiber, which can lower cholesterol levels and reduce the problems related to heart disease.
Antioxidants:
Oats also contain unique antioxidants called avenanthramides, which protect
body cells against damage due to free radicals. This means oats might even help reduce the risk of certain diseases.
Oats and Celiac Disease: Does Oat Contain Gluten?
Oats themselves are naturally gluten-free grains. However, the concern surrounding oats in the context of celiac disease stems from potential cross-contamination during processing. Mills that handle oats often process gluten-containing grains like wheat, barley, and rye, leading to the risk of gluten contamination.
Recent research has shed light on the safety assessment of oats for people having most individuals with celiac disease. Studies have shown that uncontaminated oats are generally well-tolerated and safe for consumption in controlled amounts.
What is Cross-Contact?
Cross-contact can occur at various stages, including harvesting, storing, transporting, and processing oats. This poses a significant challenge for people with celiac disease, as even trace amounts of gluten can trigger adverse reactions.
Use Certified Gluten-Free Oats in Case of Celiac Disease:
Specialized gluten-free oats are grown, harvested, and processed in dedicated facilities to reduce the risk of cross-contamination. These oats undergo stringent testing to meet gluten-free standards, providing a safe option for celiac patients.
While oats labeled as gluten-free offer reassurance, debates persist regarding the safety of mechanically cleaned oats, which may still contain traces of gluten. Further research is needed to clarify the risks associated with these products and their suitability for individuals with celiac disease.
For those with celiac disease, a cautious selection of oats is essential. Opting for oats labeled as "pure," "uncontaminated," or "certified gluten-free" can minimize the risk of gluten exposure. To ensure safe consumption, consulting healthcare professionals before introducing oats into the diet is advisable.
Research Findings:
Some research shows that most people with celiac disease can eat pure oats without any problems. These oats are made of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which can benefit health. But there's still some uncertainty. Some studies suggest that a few people with celiac disease still have issues with oats. They might react to a protein in oats called avenin, even though it's not the same as gluten.
Can Celiacs Eat Oats? Recommendations and Guidelines for Eating Oats: 
Health organizations, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Canadian Celiac Association, provide guidelines for the safe consumption of oats by individuals with celiac disease. These guidelines emphasize the importance of choosing pure, uncontaminated oats and monitoring for adverse reactions.
When incorporating oats into a gluten-free diet, it's essential to start gradually and monitor for any symptoms. Working closely with healthcare providers and dietitians can ensure a smooth transition and optimal management of celiac disease.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, oats can be a valuable and healthy option for the diet of individuals with celiac disease when consumed in moderation and in their pure, uncontaminated form. While caution is warranted due to the risk of contamination, properly selected and prepared oats can provide dietary variety and improve the overall quality of life for those with celiac disease. Always consult with healthcare professionals before making significant dietary changes, and remember to prioritize safety and well-being when navigating food choices with celiac disease.




